Insurance News Topic Modeling and Clustering
Click HERE to see the full and detailed script
Table of Contents
- Project Overview
- Objectives
- Data Preparation
- Topic Modeling
- Advanced Modeling Techniques
- Evaluation Metrics
- Results
- Applications in the Insurance Industry
Project Overview
This project aims to use NLP to categorize and understand insurance news articles scraped from a news website. The goal is to use NLP to derive actionable insights and trends from these articles that could inform business decisions. LDA, which stands for Latent Dirichlet Allocation, helps in capturing underlying themes in the data which might not be immediately apparent. These themes can be crucial in understanding behavior or trends that are predictive of certain outcomes. Advanced analysis was conducted to improve upon the baseline LDA model, by adding a K-means cluster and later a BERT model.
Objectives
- Webscrape and collect news articles and store in Amazon S3.
- Perform topic modeling using LDA model and improve upon baseline using K-means Clustering and BERT.
- Evaluate its performance using various metrics such as topic coherence and silhouette score.
- Visualize the word importance per topic and summarize each articles using BART.
Data Preparation
Data and Web Scraping
- The data was collected from
https://www.insurancejournal.com/news/national/, an insurance journal news website. - Utilized
BeautifulSoupto scrape news articles. - Converted scraped articles into a parquet format.
Data Storage
- Used
boto3 APIto save scraped data into S3 buckets. - Credentials were securely managed using .env files. This allows users to retrieve credentials without hard-coding them.
- To enure the code runs, you must have a .env file in the same directory as other files, and that you provide your AWS access key and secret key.
Data Cleaning and Vectorization
- Used
Spacyto lemmatize and keep only alphanumeric words, filtering out unnecessary characters and words. - Applied
Count Vectorizerto convert articles into numerical vectors.
Topic Modeling
LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation)
- Applied
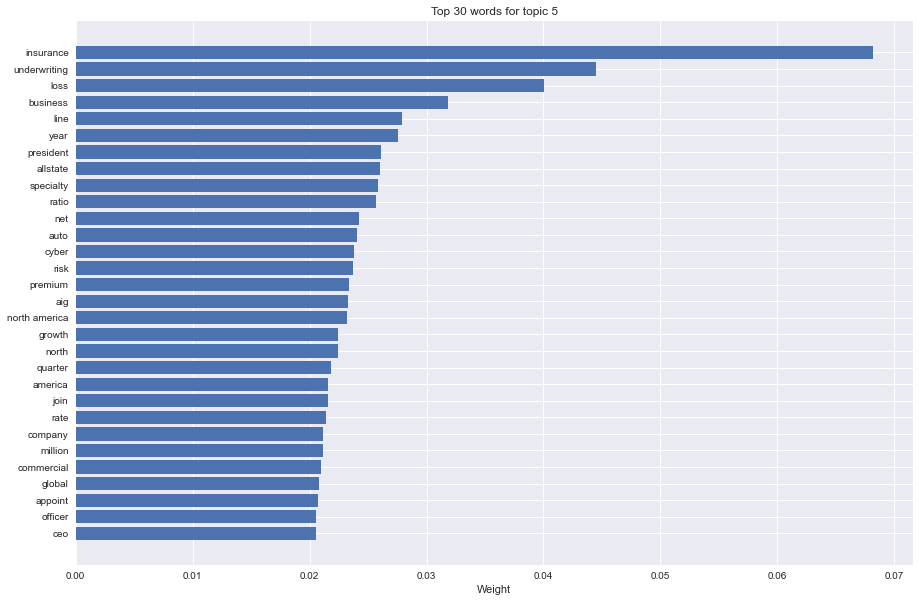
LDAto create a topic distribution matrix and identified the most probable topic for each document. Classified text documents into multiple topics. - Generated
word plotsto understand the relevance and importance of each word to its topic.
Evaluation Metrics
Silhouette Score: Measures the similarity of each sample in one cluster to the samples in the neighboring clusters.Topic Coherence: Measures the semantic similarity between high-scoring words within a topic.Topic Diversity: Measures how distinct each topic is compared to the others, aiming for more diverse topics.
Advanced Modeling Techniques
K-means Clustering: Used K-means clustering on the document-topic matrix to further segment articles. K-means clustering was used to refine the LDA topics and find nuanced groupings.
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Applied BERT and combined its embeddings with LDA topics and K-means clusters to create more contextual embeddings.
UMAP (Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection): Used UMAP to reduce the feature space of BERT embeddings for easier computation and analysis. Hyper-parameter tuned the components to find the most useful components for clustering.
BART (Bidirectional and Auto-Regressive Transformers): Used BART to generate summaries of each article to summarize the articles for easier understanding and verification.
Results
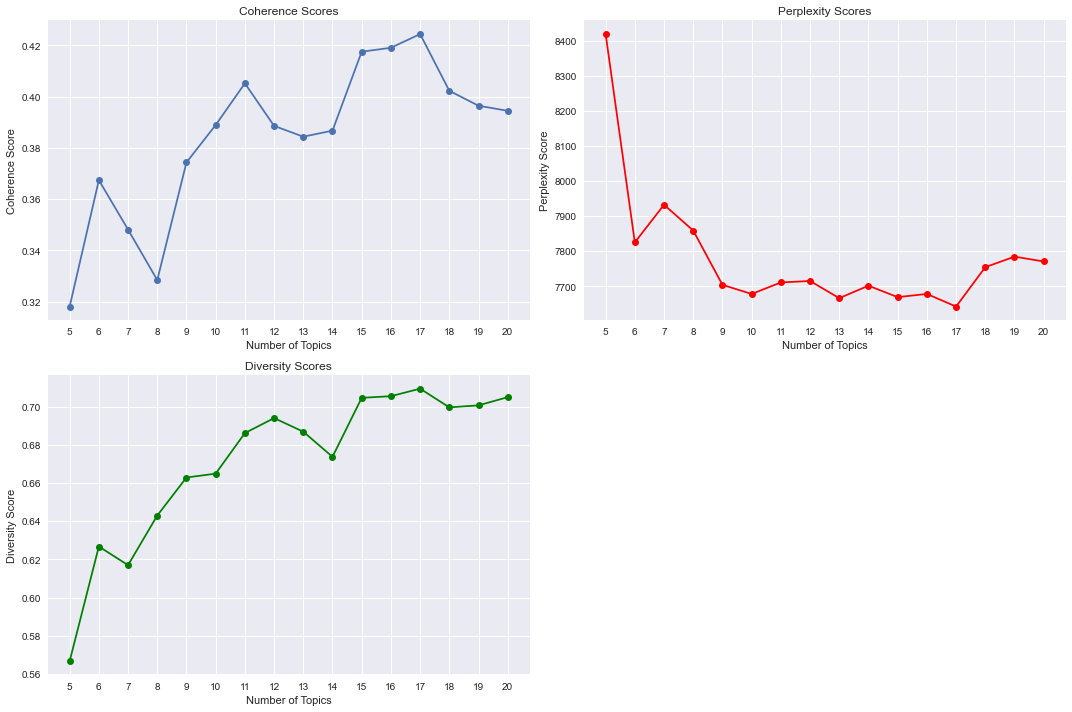
Upon calculating topic coherence, diversity, and perplexity score for LDA, 17 was a reasonable topic number to choose. From the plot shown below, topic coherence and diversity scores are at maximum, and perplexity score is at minimum when topic number equals 17.
To improve upon the current LDA model, several other models were implemented. Here were the combinations of models that I mixed:
- LDA
- LDA + K-means
- LDA + K-means + BERT
The metrics were as following:
| Model | Topic Coherence | Topic Diversity | Silhouette Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | 0.4064 | 0.739 | N/A |
| LDA + K-means | 0.4135 | 0.7417 | 0.4928 |
| LDA + K-means + BERT | 0.4934 | 0.7725 | 0.4034 |
Results showed that combining K-means and BERT to LDA model improved the topic coherence and diversity score. However, I also noticed that adding BERT to the LDA + K-means model actaully lowered the silhouette score. Further exploration is needed to find out why.
There is a caution when using K-means clustering because K-means clustering uses distance based method for clustering, and the document-topic matrix is not a vector but a probability distribution of topics for each document. A standard K-means clustering may not capture the signals in the document well. Rather, using a probability distribution based clustering may be better (such as Jensen-Shannon Divergence).
Applications
The topics generated from this project can be invaluable for business strategy in the insurance sector (and many others). Understanding what themes and issues are prevalent in insurance news can guide companies in their marketing strategies, product development, and customer engagement efforts.
-
Behavioral Differences: Once these clusters are identified, the researchers can further study if there are differences in customer behavior across these clusters. For example, the “fire related claims” cluster might have a higher loss ratio compared to the “storm related claims” cluster. -
Tailored Marketing: Companies can use this information for targeted marketing. If a user falls into the “fire related claims” cluster, they might receive more focused ratings that deals with fire claims. -
Feature Engineering: One of the challenges with textual data is that it’s inherently unstructured, making it difficult to use in traditional predictive models. LDA transforms this text into structured numerical data in the form of topic probabilities for each document. The topics, which used to be text data and now numerical data, can then be used as features in predictive models.